Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic Cancer
The cost of treating pancreatic cancer in India varies. Now it’s easy to calculate the cost based on the number of sessions you need
What Is Pancreatic Cancer?
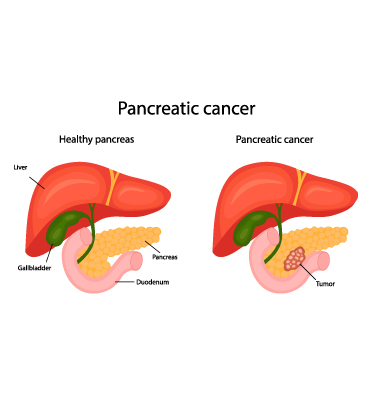
Cancer is currently the most prevalent disease, not only in India but across the globe. Pancreatic cancer, in particular, poses significant challenges due to the vital role of the pancreas in digestion and metabolism. The pancreas is a crucial organ responsible for the secretion of bile, a key component facilitating the digestion of various nutrients like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Additionally, it releases two essential hormones, insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels in the body. Beyond aiding digestion, the pancreas plays a pivotal role in energy production by metabolizing glucose, breaking it down into its simplest forms to release energy.
However, when pancreatic cancer develops, it disrupts all these functions. Recent studies and research indicate that pancreatic cancer constitutes approximately 3 percent of cancer cases in the United States, contributing to nearly 7 percent of cancer-related deaths.
Pancreatic cancer may be largely divided into two broad types:
- Pancreatic Adeno-Carcinoma
- Stage 4 (Metastatic Breast Cancer Stage)
Pancreatic Neuro-Endocrine Tumors
This cancer variety emerges from hormone-secreting endocrine cells responsible for regulating metabolism and mood control.
There is no size of the tumor in Stage 4. The cancer has become well- developed by this stage and has affected the surrounding lymph nodes, the organs, and some other parts of the body too.
Symptoms Of Pancreatic Cancer
The symptoms of pancreatic cancer can vary from person to person, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms in the early stages. However, there are certain common signs associated with pancreatic cancer often observed in those affected. Some of these symptoms include:
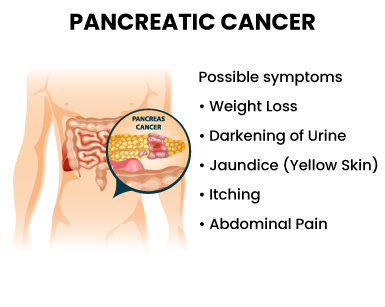
- Jaundice
- Lack of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Unexpected weight loss
- Pain in the lower back region
- Feeling of itchiness in the skin
- Discolored and greasy stool
- Mild to severe pain in the abdomen
- Chances of getting clinical depression
- Type 2 diabetes or high levels of blood sugar
- The color of urine changes from dark to brown shades
- Blood clots or thrombosis that usually occurs in body parts such as legs, hands etc and appears red along with swelling and pain in that region
Causes Of Pancreatic Cancer
Multiple factors are associated with the development of pancreatic cancer, including:
1. Excessive weight gain and obesity, which can heighten the risk of pancreatic cancer.
2. Individuals with diabetes, both type 1 and type 2, are at an increased risk of pancreatic cancer.
3. Heavy alcohol consumption or drug abuse may lead to pancreatitis, potentially increasing the risk of pancreatic cancer.
4. Prolonged smoking of cigarettes, which contain toxic substances like tar and nicotine, is a known risk factor for various cancers, including pancreatic cancer.
Infections caused by microorganisms such as H. pylori in the digestive tract may contribute to the development of pancreatic cancer.
Unhealthy dietary habits and an irregular lifestyle can also increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Consuming junk foods that are processed within the body may harm the pancreas significantly.
Furthermore, recent research, studies, and experimental data suggest that hereditary factors can play a role in the likelihood of developing pancreatic cancer. People with a family history or genetic traits related to conditions like Lynch syndrome, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, multiple mole melanoma syndrome, and others may have an increased risk of pancreatic cancer due to genetic mutations and recombinations.
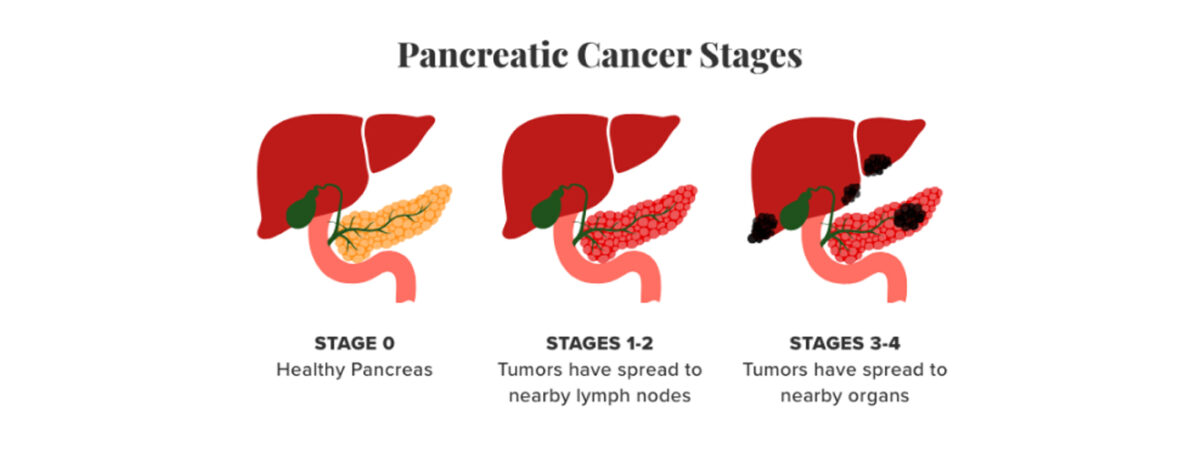
Stages Of Pancreatic Cancer

- Pancreatic cancer stage 4
- Pancreatic cancer stage 3
- Pancreatic cancer stage 2
- Pancreatic cancer stage 1
- Pancreatic cancer stage 0
Stage 4 represents the most advanced and challenging phase of pancreatic cancer, offering little hope for patient survival and recovery. During this stage, symptoms become increasingly pronounced and easily discernible. When diagnosed at such a late stage, specifically in the 4th stage, the chances of recovery from pancreatic cancer are extremely slim. Common symptoms in this stage encompass:
1. Loss of appetite
2. Persistent fatigue and exhaustion
3. Unexplained and significant weight loss
4. Increased risk of clinical depression
5. Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the eyes, nails, and skin
6. Mild to severe pain in the upper abdomen and lower back
Pancreatic cancer becomes particularly challenging to address by stage 3, and achieving a cure becomes increasingly difficult. During this stage, patients may begin to experience the following symptoms:
1. Unexplained weight loss
2. Feelings of depression
3. Lower back pain
4. Loss of appetite
5. Persistent exhaustion and severe fatigue
6. Pain or tenderness in the upper abdomen
While treating stage 3 pancreatic cancer is indeed a formidable task, many surgeons in India have successfully managed this stage through the skillful application of radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
In this stage of pancreatic cancer, the tumor has grown in size and begun to extend into its surrounding regions. Depending on the tumor's size, this stage can be further divided into two sub-stages:
Stage 2A: The tumor measures larger than 4 centimeters (cm) but has not yet invaded the surrounding areas or nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: The tumor has commenced spreading into adjacent tissues and has affected approximately 2 to 3 lymph nodes.
Stage 2B.The tumor has either increased in size and has become more than 5 cm and may or may not spread into the lymph nodes.
This stage marks the initial phase of cancer development, with a small tumor beginning to form on the pancreas. It can be broadly categorized into two phases:
Stage 1A: In this stage, the size of the pancreatic tumor is 2 cm or smaller.
Stage 1B: The tumor has grown slightly larger, measuring more than 2 cm but less than 4 cm.
Stage 0 of pancreatic cancer typically presents no noticeable symptoms, as it represents the earliest phase of development. During this stage, the condition hasn't progressed to a full-blown cancer, but abnormal cells may begin to form within the organ and its vicinity, potentially evolving into cancerous cells over time.
Treatments Of Pancreatic Cancer
The treatment of pancreatic cancer is contingent on several factors, including the cancer’s stage, the extent of damage to the pancreas and surrounding areas, and other pertinent considerations. However, the fundamental approach to treating pancreatic cancer involves two primary objectives:
1. Eliminating the cancerous cells to halt their abnormal division.
2. Preventing the cancer from metastasizing to other parts of the body.
While the specific type and methods of treatment for pancreatic cancer can vary among individuals, there are common approaches to its treatment. Some of these conventional treatment methods include:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
The predominant method of addressing pancreatic cancer involves surgical intervention. The primary goal of pancreatic cancer surgery is to eliminate the portions of the pancreas that have been affected by the cancer. This approach is instrumental in effectively removing the tumor or mass associated with the cancer. However, it is essential to note that if the cancer cells have extended from the pancreas into the neighboring regions, the removal of those affected areas becomes challenging. Consequently, in cases where pancreatic cancer has reached an advanced stage, surgery is not typically the preferred option for treatment.
Radiation therapy is a highly effective approach for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. This method employs X-rays and high-intensity light beams that are directed at the afflicted area to eradicate the cancer cells.
In cancer treatment, drug therapy is a highly effective approach that utilizes medications to address the cancer.
This is a unique therapy to treat pancreatic cancer. In this method, the cancer cells are targeted, and they are destroyed by using medicinal drugs and antibodies, without damaging the surrounding healthy cells.
Immunotherapy is an advanced approach in cancer treatment, as it involves enhancing the body's immune system to combat the disease.
Breast Cancer Diagnosis
6. MRI Scans of the Breasts: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans can offer comprehensive views of breast tissue.
Adhering to these diagnostic methods and your healthcare provider’s guidance is crucial for an accurate assessment of breast cancer.
For the accurate diagnosis of breast cancer, specific methods should be diligently followed. Your healthcare provider may recommend a series of steps, lifestyle adjustments, and a range of tests, including:
1. Mammogram: A mammogram is a common screening test for detecting breast abnormalities.
2. Biopsy: A biopsy involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the breast for examination under a microscope.
3. Breast Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging of the breast can provide detailed images of breast tissue.
4. Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes: This ultrasound assesses the lymph nodes in the breast area.
5. Necessary Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to assess specific markers or indicators associated with breast cancer.
Survival Rate In Pancreatic Cancer
Survival rates in case of pancreatic cancer can vary from one person to the other, depending on the stage of the cancer and its severity. Here is the average survival rate for pancreatic cancer.
| Stage | 1-year survival rate | 5-year survival rate | 10-year survival rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Localized | 55% | 35.4% | 29.8% |
| Regional | 50.6% | 12.3% | 8.1% |
| Distant | 17.4% | 2.8% | 1.6% |
Pancreatic Cancer Treatment In India
Many countries around the world are renowned for their medical tourism offerings, and India stands out among these nations. Among the 36 JCI (Joint Commission International) accredited hospitals, MGM Healthcare, MIOT Hospital, and the Fortis network are highly regarded for their pancreatic cancer treatment services in India. This recognition is attributed to their competitive treatment costs, state-of-the-art infrastructure, skilled medical professionals, and support staff.
FAQs
In situations where pancreatic cancer has advanced to a severe and challenging-to-treat stage, patients are placed under palliative care. This specialized care focuses on ensuring the patient’s utmost comfort and well-being, particularly when the patient’s condition is critical.
Best Hospitals for Orthopaedic Surgical Oncology in India
Fill this form to get a free quote from best hospitals in India


At MediTours India, we stand as a distinguished leader in the realm of medical tourism, dedicated to transforming your healthcare journey into a seamless and transformative experience. With a commitment to excellence and a focus on your well-being, we pave the way for a new era of medical travel.
Contact Us
Address : C603 Jalaram Park LBS Road. Bhandup West Mumbai -400078 Phone : +91 9820344697 Email : ajit@meditoursindia.in
Copyright by indiameditours 2023. All rights reserved.








































