Retinoblastoma Cancer
Retinoblastoma Cancer
What Is Retinoblastoma Cancer?
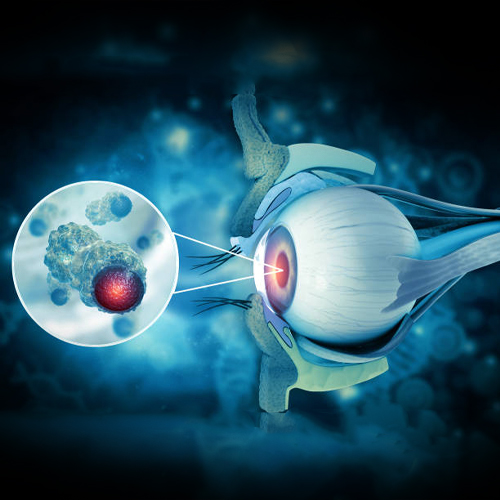
Retinoblastoma cancer is a malignancy primarily located in the retina, a crucial part of the eye. This form of ocular cancer is predominantly found in children and infants under the age of 2 or 3. While the chances of developing retinoblastoma cancer after the age of 6 are rare, it can occur in older children, albeit infrequently.
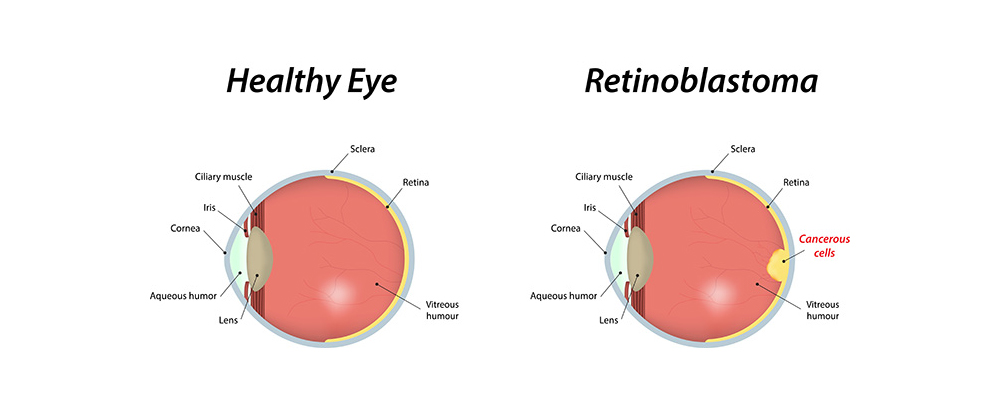
The retina is a vital component of the eye composed of nerve cells and sensory tissues. It resides within the inner part of the eye and plays a fundamental role in receiving light rays and transmitting visual information to the brain through the optic neurons. Although retinoblastoma is a rare cancer, like other forms of cancer, it can become life-threatening if left untreated for an extended period.
Retinoblastoma typically manifests as a cancerous lump or tumor that gradually forms and spreads throughout the eye, ultimately affecting vision. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention are crucial for effectively managing this condition and preserving the child’s eyesight.
Retinoblastoma cancer is indeed known for its occurrence in both eyes and its potential to disrupt eyesight in young children. However, it’s essential to emphasize that early detection is key to successful treatment and a positive outcome. With timely diagnosis, various treatment approaches, including surgery and chemotherapy, are available to effectively manage retinoblastoma in children.
The prognosis for retinoblastoma is generally favorable when identified and treated promptly. Regular eye examinations and awareness of common signs and symptoms can help ensure that the disease is detected early, allowing for the best possible treatment and outcome for affected children.
Types Of Cancer
Cancer can be classified into several major categories, including but not limited to:
Carcinoma represents a form of cancer originating in the skin or the lining of organs, such as the liver or kidneys. Carcinomas are characterized by the proliferation of abnormal cells with unregulated division. While they have the potential to metastasize to different areas of the body, this doesn’t always occur. Carcinoma can be subdivided into various subtypes, including basal cell carcinoma, transitional carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Sarcoma is a type of cancer that can manifest in various anatomical regions. It serves as a comprehensive term encompassing a diverse array of cancers originating in both bones and soft tissues. Sarcomas specifically take root within connective tissue, which consists of cells that provide structural support and linkage to other tissue types in the body. These tumors most frequently occur in the bones, muscles, tendons, cartilage, nerves, fat, and blood vessels of the arms and legs, although they can potentially develop in any part of the body.
Leukemia is a form of cancer that affects the body’s blood-forming tissues, which encompass the bone marrow and the lymphatic system. It manifests in various types, with some being more prevalent among children. Common symptoms associated with leukemia include swollen lymph nodes, recurring nosebleeds, fatigue, frequent infections, weight loss, bleeding issues, and bone pain.
These two closely linked malignancies share a common lymphoid origin. They are both forms of cancer that impact cells within an individual’s bloodstream, typically originating from the immune system’s cells.
Germ cell tumors are a type of neoplasm that develops from germ cells, which are the cells responsible for producing eggs in females and sperm in males. These tumors can occur in various parts of the body, including the ovaries and testes, as well as other locations such as the mediastinum or brain. Germ cell tumors can be benign or malignant, and they often require medical intervention for diagnosis and treatment.
A blastoma is a category of cancer, frequently observed in children, resulting from the malignant transformation of precursor cells, often referred to as blasts. Some examples of blastomas include nephroblastoma, medulloblastoma, and retinoblastoma.
Symptoms Of Rhetinoblastoma Cancer
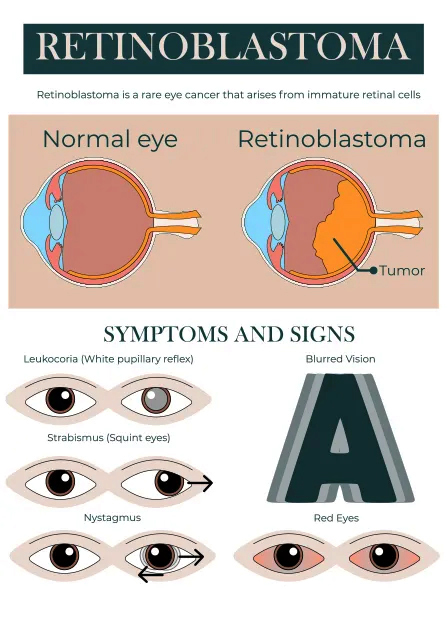
Just like any other form of cancer, retinoblastoma cancer also does not show any kind of significant or noticeable symptoms in the early stages. So, it becomes quite difficult to make out whether a child has been affected by retinoblastoma cancer. The symptoms start to occur in the body at the later stages but by that time the disease has already spread to a huge extent and it requires a major effort on the part of the health care experts and concerned oncologists to treat the disease at such advanced stages. But there are certain common symptoms of retinoblastoma cancer. Some such symptoms are as follows:
- Lack of proper vision
- Pupils remain wide open
- Mild to severe pain in the eye
- A crossed eye syndrome starts developing in the child
- The size of the pupil will become abnormally enlarged
- The shape and size of the eyes appear larger and weird than normal
- The pupil gradually turns white and the normal black or brown color of the pupil starts disappearing or fades away slowly
- The color of the iris changes
- A temporary squint of the eyes
- Constant irritation in the eyes
- The color of the center of the eyes starts fading away, forming a cloudiness
- The color of the eye may turn red- this might occur either in one or both the eyes
- The eyeballs do not move equally focus on one particular direction
- Eye blood vessels at the back do not reflect the red color due to the formation of the cancerous tumor
Stages Of Rhetinoblastoma Cancer
Just similar to other forms of cancer, retinoblastoma cancer has also been divided into 4 stages by oncologists and health care experts, depending upon several factors such as the severity of the disease, treatability of the disease, condition of the patient, and many others. The different stages of retinoblastoma cancer can be listed here as follows:
This is the very first stage of cancer when the disease has just started affecting the eyes and has just entered the retina.
In the second stage of the retinoblastoma cancer a tumor has started developing within the eye and has started affecting the child’s vision.
Cancer has started spreading into the surrounding areas of the eye, such as the pupil, iris, and many other portions, and has started damaging the neurons.
This is the most dangerous stage of retinoblastoma cancer when the cancer is quite difficult to treat and has already damaged most of the eyesight of the child.
Causes Of Retinoblastoma Cancer
The primary cause of retinoblastoma cancer in children is indeed believed to be genetic mutations and recombination that occur early in a child’s development, even before birth. Retinoblasts are the precursor cells that begin developing in the eyes of a baby prior to the full maturation of the retina. Genetic abnormalities and uncontrolled, abnormal growth of these retinoblast cells can lead to the development of retinoblastoma cancer in a child.
These genetic mutations can occur sporadically or may be inherited from a parent who carries the genetic mutation associated with retinoblastoma. In cases of hereditary retinoblastoma, the child inherits a mutated gene from one or both parents, which significantly increases the risk of developing the cancer.
Early detection and genetic counseling for families with a history of retinoblastoma are crucial in managing the condition and assessing the risk for affected children and future generations.
Diagnosis Of Retinoblastoma Cancer
Diagnosis occupies an important part of treating any kind of cancer. Proper diagnosis is the only way that helps in the proper and correct treatment of the disease. For treating and the diagnosis of the retinoblastoma cancer disease in the body, your concerned oncologists and health care experts might advise you to undergo certain necessary tests related to the retinoblastoma cancer that will effectively help to detect cancer. Some of the diagnosis-related tests and procedures are as follows:
An ultrasound is a test that is carried out to check the growth of cancer cells and the development of the tumor with the use of ultrasound waves.
A CT scan is another such test that uses a highly- advanced infrastructure of computerized machines that takes an image of the retina and the inside of the child’s body to check how far cancer has spread. In this method of diagnosis, a medication, in the form of a chemical dye is used to inject into the blood veins to get a clear picture of the cancer growth.
An MRI is a very common test used for the diagnosis of cancer that uses a high-intensity magnetic field, to get clear pictures of the brain, eye, and spinal cord. This test can also tell whether retinoblastoma cancer has affected the eyesight of the child.
This is another test that takes photographs of the brain and the nervous system that joins the brain and the eyes. This test is quite necessary to detect the growth of retinoblastoma cancer in a child’s body.
Blood tests are quite crucial for the diagnosis of retinoblastoma cancer. A blood test helps to know the blood profile of the cancer-affected child and measures the count of red blood cells or RBC, white blood cells or WBC, and platelets that are quite necessary before beginning the surgery or chemotherapy.
Treatment Of Retinoblastoma Cancer
Surgery is the most commonly used and the most- recommended procedure to treat retinoblastoma cancer among children. Through surgery, the oncological surgeon destroys the cancer cells and removes the affected- cells in the retina of the affected eyes.
The most common way of treating cancer is the use of chemotherapy. This method is very commonly prescribed by physicians and oncologists sometimes it is done after the surgery. In this method, the doctors use chemicals, drugs, and surgical medications to destroy the cancer cells and those areas that have been affected by retinoblastoma cancer. Chemotherapy occupies an important part of pediatric oncology that helps to completely reduce the growth of tumors and cancer cells in the retina of the child’s eyes through some procedures such as:
- Cryotherapy
- Radioactive plaque therapy
- Thermotherapy or photocoagulation (laser therapy)
In radiation therapy, a beam of high-intensity light rays is applied to cancer-affected areas within the retina to destroy the cancerous cells inside the eyeballs and to provide a more clear vision by removing the affected cells.
This method is usually prescribed and used by oncologists and health care experts to treat retinoblastoma cancer to destroy the targeted cancer cells in the retina through the application of medical drugs.
Side Effects Of The Treatment Of Retinoblastoma Cancer
The procedures that are recommended by oncologists and health care experts to treat retinoblastoma cancer might lead to the occurrence of several types of side effects in children after the treatment is done. Some of the side effects are as follows:
- Feeling of drowsiness.
- Excessive tiredness and exhaustion.
- Difficulties in normal growth and development.
- The feeling of nausea, which may or may not be accompanied by vomiting.
- Mild to severe headache, that commonly occurs after having radiation therapy.
If you feel that your child is having any of the above side effects, then it is highly advisable to take the help of the concerned health care expert at once.
FAQs
A child with retinoblastoma cancer can surely recover after treatment if the disease is detected and treated early.
It is quite difficult to prevent retinoblastoma cancer because the disease occurs through abnormality in genetic mutation.
The concerned physician is the best person to advise how to protect your child’s eyes from retinoblastoma cancer.
Regular check- ups and strictly following the instructions of the physicians are the things to be done after the treatment of retinoblastoma cancer.
The time taken to cure this type of cancer entirely depends on the treatment procedures recommended for the patient and of course, on the severity of the patient.
Fill this form to get a free quote from best hospitals in India


At MediTours India, we stand as a distinguished leader in the realm of medical tourism, dedicated to transforming your healthcare journey into a seamless and transformative experience. With a commitment to excellence and a focus on your well-being, we pave the way for a new era of medical travel.
Contact Us
Address : C603 Jalaram Park LBS Road. Bhandup West Mumbai -400078 Phone : +91 9820344697 Email : ajit@meditoursindia.in
Copyright by indiameditours 2023. All rights reserved.